ACCELERATE OPTICS AND PHOTONICS INNOVATION AND DESIGN
End-to-End Multiphysics and Multiscale Simulation Platform
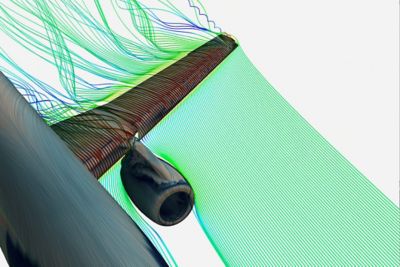
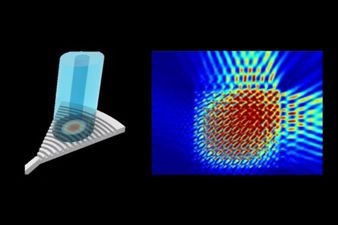
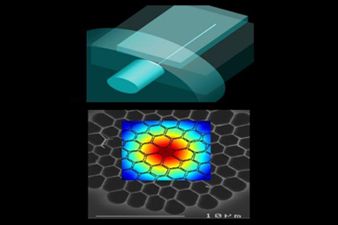
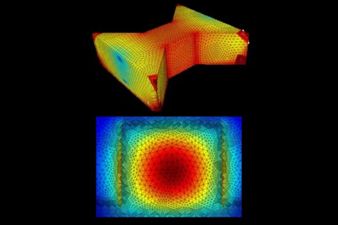
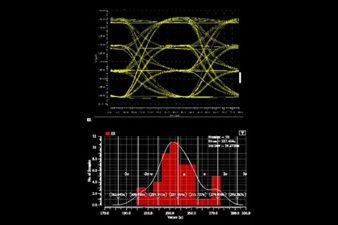
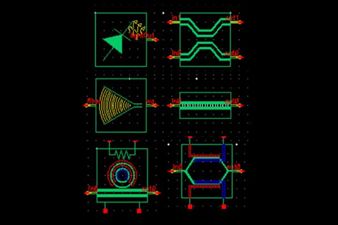
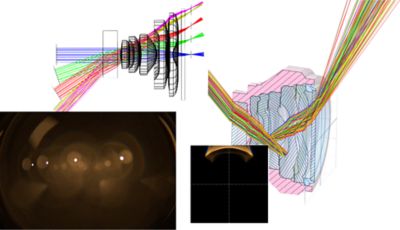
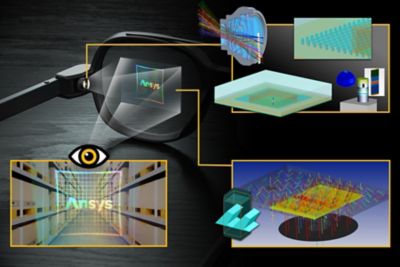
Ansys Optics solutions offer robust design, optimization, and verification simulation software backed by world-class support. These tools empower designers to expedite the development of groundbreaking optical products while improving performance, reliability, and yield. With a suite of top-tier physics solvers, Ansys Optics provides user-friendly workflows for precise multiscale system design, from the nano to macro scale, enabling the design of diverse applications across various industries.