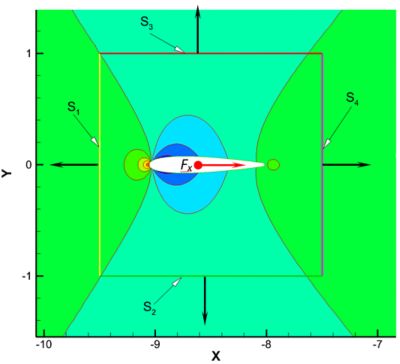
Estimation of Airfoil Drag using RTT and Ansys Fluent Software
The Reynolds Transport Theorem (RTT) is applied to calculate the total force, pressure force, and viscous force acting on an airfoil at a zero-degree angle of attack. These analytical estimates are then compared with Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) predictions obtained using Ansys Fluent®, computational fluid dynamics software. For this study, Fluent simulations are conducted for a flow with Mach number (Ma) = 0.6 over a NACA 0012 airfoil. The RTT-derived total drag, pressure drag, and viscous drag values show deviations of only 1.66%, 1.42%, and 4.2%, respectively, from the CFD predictions. Such close agreement demonstrates the reliability of RTT as a theoretical tool while also highlighting the capability of CFD to capture detailed aerodynamic effects. This combination reinforces the importance of CFD in modern engineering analysis and provides a strong link between theoretical predictions and numerical simulations
Learning Outcomes
- Validation of applicability of Reynolds Transport Theorem in computing body drag
- Setting up Ansys Fluent simulations and results to obtain body drag
- Understanding the importance of validating the theorical and computational values.
Applicable Courses for Use
- Fluid Mechanics
- Computational Fluid Dynamics
- Advanced Fluid Mechanics
- Aerodynamics
- Industrial Aerodynamics
- High Speed Aerodynamics
Downloadable Content
- Case Study pdf
- Mach-0.6-final-sb.cas
- Mach-0.6-final-sb.dat
Related Resources
Flow around an Airfoil with Ansys Fluent | Education Resource
Transonic Aerodynamics in Ansys Fluent | Education Resources
Supercritical Airfoils in Ansys Fluent | Education Resources