-
-
학생용 무료 소프트웨어에 액세스하기
차세대 엔지니어에게 힘을 실어주는 Ansys
학생들은 세계적 수준의 시뮬레이션 소프트웨어를 무료로 이용할 수 있습니다.
-
지금 바로 Ansys에 연결하십시오!
미래를 설계하기
시뮬레이션이 다음 혁신을 어떻게 지원할 수 있는지 알아보려면 Ansys와 연결하십시오.
국가
무료 트라이얼
제품 및 서비스
학습하기
회사 정보
Back
제품 및 서비스
We have all seen videos and images of rockets at liftoff, ascending into space as plumes of fire and smoke trail behind them. This is the image we conjure when we think of traveling to space, and it's been the standard method of space travel for decades. However, once in orbit, the rocket relies on a limited amount of fuel to complete its mission. There’s no denying that many things can go wrong in space. With that in mind, what if a more sustainable mode of space transportation could be developed?
Imperial College Space Team
Project Svarog, named for the Slavic god of fire and sky, is a student team from Imperial College London with the goal of becoming the first student team to send a spacecraft outside the solar system. To achieve this, the team has chosen to further advance solar sail technology.
Solar sails are a unique method of space exploration that is not yet widely used. A solar sail does not require a propulsion mechanism or fuel. Instead, it uses the solar radiation pressure of light particles (photons) from the Sun. It travels through space by harnessing this free energy, much like how a sailboat uses the wind to propel itself. The reflective surface of a solar sail and its ability to swivel allow it to capture the maximum amount of light based on its position. As a result, this method of space travel is significantly more sustainable and reliable.
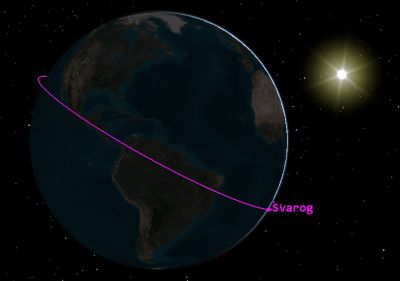
Ansys Systems Tool Kit (STK) digital mission engineering (DME) software simulation of Project Svarog’s solar sail in low Earth orbit (LEO) trajectory over Africa
The team aims to utilize a specific solar sailing trajectory known as sun diving to depart from our solar system. Sun diving refers to the act of approaching the sun very closely, diving into its rays. By harnessing the intense solar radiation pressure, the object involved can experience significant acceleration. This allows it to spiral away from the sun, effectively raising its apogee at a much faster rate.

BEXUS 34 solar sail prototype test deployment two days before launch
The team was founded in 2021 as part of the Imperial College Space Society. “Today, Project Svarog has approximately 25 active members, all of whom are Imperial College students. By the nature of their degree, they can only really stay with the project a couple of years before they graduate,” says second-year doctorate student Matthew Acevski, the team’s mission leader. Through these changes, the project leads ensure continuous progress in all areas by consistently recruiting and replenishing sub-teams.
Despite the rotation of students, the team has not lost sight of its goal: getting to space. “We’d love to do it in the next six to eight years,” says Acevski.

Project Svarog team leads pictured three weeks before the BEXUS 34 launch, which involved a thermal vacuum chamber test of the team’s first solar sail prototype in Kiruna, Sweden.
Project Svarog Joins With REXUS/BEXUS
The team has participated in one full REXUS/BEXUS campaign (2023-2024). The team was accepted again for the current 2024-2025 campaign with the goal of developing all of their subsystems into a fully functional CubeSat. The program involves sending student-designed experiments into the far reaches of the atmosphere in either a rocket (REXUS) or weather balloon (BEXUS). The program is a joint effort between the German Aerospace Center (DLR) and the Swedish National Space Agency (SNSA) in collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA) that seeks to further scientific research through the use of rockets and balloons.
The team launched their preliminary design on the BEXUS balloon, approximately 30 km above the Earth’s surface, into low Earth orbit (LEO), for data collection. During the balloon’s flight, which can last anywhere from three to five hours in total, the team was able to conduct experiments in near-space conditions with low atmospheric pressure.
Journeying to Space With Simulation
Throughout the project, the consistent use of simulation has been a key element in successfully researching and developing the solar sail. The team members use Ansys tools for mechanical simulations and their plan is to increase the use of simulation as the project progresses.
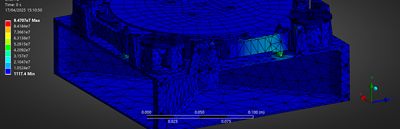
“We utilized Ansys Mechanical via Workbench to perform critical launch environment simulations, including modal, quasi-static, random vibration, and shock analyses,” says Golf Rojnuckarin, head of structures simulations with Project Svarog. “A key advantage of Ansys Workbench was its seamless integration capabilities. This allowed us to efficiently combine and manage various load cases, such as superimposing random vibration with quasi-static loads, significantly streamlining our workflow. The integration with Ansys Granta also provided immediate access to an extensive material database, which are properties specific to our needs.”
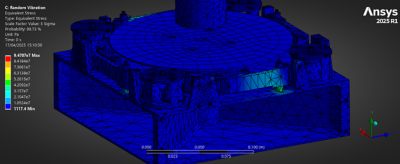
A modal analysis shows the deformation of each mode under load. The colors indicate how much stress each point of the CubeSat is under at any given time. This information is vital in understanding where failure is most likely to occur.
The Project Svarog team will continue to harness the capabilities of Ansys simulation software to model and test the solar sail's structural, mechanical, and fluid characteristics as they get closer to launching into space.
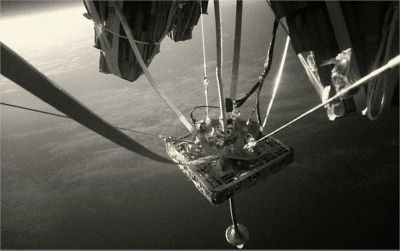
Image from a camera on the BEXUS 34 balloon while in flight at an altitude of 27 km above Earth’s surface. The hub is being hung from the underside of a large gondola (provided by Swedish Space Corp.), which is being supported by a large stratospheric balloon.
A significant enhancement in the upcoming prototype, aimed to demonstrate and record the deployment of a CubeSat form factor solar sail membrane, is the integration of tape spring booms in a single-spool configuration. The updated design employs new and improved booms with a more reliable deployment system. . By using a single central cylinder to deploy the booms, the mechanism requires less space, enabling a more compact form factor suitable for CubeSat applications. These changes represent a major improvement in both performance and design efficiency.
On the Horizon
As the Project Svarog team continues to evolve, they seek opportunities to put their solar sail technology into orbit. Their dedication to innovation drives them to explore new methods and designs to refine the efficiency and functionality of their systems. Through these efforts, the team pushes the boundaries of lightweight, deployable space technology.
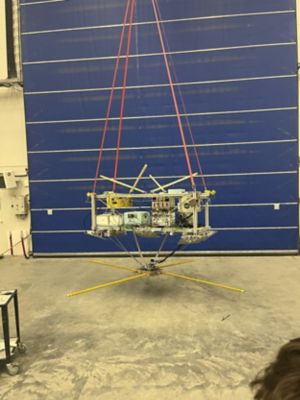
The hub that was supported by the BEXUS balloon
Project Svarog’s vision to be the first student team to send a spacecraft to the edge of the solar system is taking shape as the team inches closer to launching their solar sail into orbit. “We hope that in the coming years, the cumulative experience of all of our many experiments and missions can lead to the development of truly innovative and new improvements in solar sailing technology, which can be utilized in future space missions around the world,” says Acevski.
As the team makes significant strides in the space industry, they inspire others to see solar sailing as a viable alternative to long-duration space missions. Through their collaborative efforts with leading European space agencies, their goal is becoming a reality.
Explore an Ansys Student Team Partnership and learn how you can access Ansys software for free today.
Learn more about how simulation is used in the space sector by watching our Simulating Space documentary.
“A key advantage of Ansys Workbench was its seamless integration capabilities.”
— Golf Rojnuckarin, head of structures simulations, Project Svarog
The Advantage Blog
The Ansys Advantage blog, featuring contributions from Ansys and other technology experts, keeps you updated on how Ansys simulation is powering innovation that drives human advancement.