Case Study
“With Ansys HFSS software, we can make courses more dynamic by showing the effects of changing structure parameters in the electromagnetic fields and providing a tool for students to analyze, characterize, and design microwave antennas, circuits, and waveguides. Electromagnetic simulation allows the visualization of fields in a physical structure, bridging theory and practice in ways that equations and textbooks alone cannot, while giving students the ability to explore changes and see the effects in the structure’s response.”
— Rafael A. Rodríguez Solís
Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Puerto Rico
Dr. Rafael A. Rodríguez Solís uses Ansys HFSS software, accessed through the Ansys Electronics Desktop platform, to teach waveguide and microwave antennas concepts at skill levels ranging from undergraduate to graduate courses. Aside from its modeling and design capabilities, HFSS software enables students to visualize electromagnetic (EM) fields in structures, making it easier to teach complex concepts.
As part of a graduate special topics course, a student developed a broadband corporate feed that achieved a large bandwidth (2:1) at millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies. The design was modeled and optimized in HFSS software, which enabled the students to quickly model the power divider and optimize the design to achieve the intended performance. Later, the design was presented at the 2024 Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) International Antennas and Propagation Symposium.
Challenges
Electromagnetics tends to be difficult to understand, given the mathematical complexity and the intangibility of fields and waves. Solís wanted to supplement student learning with practical applications. Having a tool that can display EM fields in a structure while changing its geometry was very useful in aiding their understanding. Solís wanted to use software that could display 3D fields and provide powerful modeling and design capabilities.
With HFSS software, students can see field distributions in waveguides for individual modes or their combinations, helping them identify modes, design feeds, and distinguish propagating waves from standing waves. They can also visualize how discontinuities cause reflections and, in antenna design, how adjusting antenna size influences current behavior — turning abstract concepts into intuitive, hands-on learning.
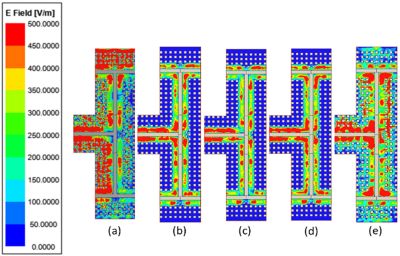
Electric field distribution for a power divider at 10 GHz (a), 20 GHz (b), 30 GHz (c), 40 GHz (d), and 50 GHz (e), showing the divider bandwidth. Note the loss of field containment in the waveguide at 10 GHz and 50 GHz.
Engineering Solutions
In his classes, Solís uses HFSS software to:
- Display fields inside waveguides
- Display currents and fields in microstrip patches and slots
- Show cutoff frequencies of different waveguide modes
- Demonstrate the difference between infinite and finite arrays
- Design microstrip antennas (patches and slots)
- Find propagation modes in periodic structures
- Teach about antenna arrays using the hybrid and array solvers
- Help students learn about propagation modes with the Eigenmode solver to analyze and design substrate-integrated waveguide structures and gap waveguides
Within the Electrical and Computer Engineering department, the courses in which Solís used HFSS software are as follows:
- INEL 4156, Applied Electromagnetics Laboratory
- INEL 5627, Antenna Theory and Design 2
- INEL 6668, Microwave Antenna Engineering
- INEL 8695, Special Topics in Applied EM: Novel electromagnetic waveguides and their applications in microwave antennas
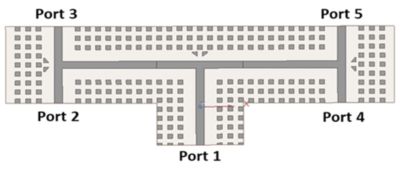
A 1-to-4 double-ridged gap waveguide power divider. Inherent impedance mismatches are created at each of the power dividers, and impedance transitions were implemented by changing the spacing between the ridges with linear tapers to eliminate the frequency dependence of the impedance behavior.
Benefits
- Use of HFSS software enabled Solís to present course material in a more dynamic way. The opportunity to show the effects of changing parameters in the structures’ behavior in real time complemented lectures.
- Students were able to develop detailed models of their antennas and circuits and perform design and characterization activities in a software environment they will most likely use in their jobs after graduation.
- Students were able to validate the theory learned in class in the same canonical examples with HFSS software, and it enabled them to understand the behavior of more complicated geometries.
现在就开始行动吧!
如果您面临工程方面的挑战,我们的团队将随时为您提供帮助。我们拥有丰富的经验并秉持创新承诺,期待与您联系。让我们携手合作,将您的工程挑战转化为价值增长和成功的机遇。欢迎立即联系我们进行交流。