-
-
Software gratuito per studenti
Ansys potenzia la nuova generazione di ingegneri
Gli studenti hanno accesso gratuito a software di simulazione di livello mondiale.
-
Connettiti subito con Ansys!
Progetta il tuo futuro
Connettiti a Ansys per scoprire come la simulazione può potenziare la tua prossima innovazione.
Paesi e regioni
Customer Center
Supporto
Partner Community
Contatta l'ufficio vendite
Per Stati Uniti e Canada
Accedi
Prove Gratuite
Prodotti & Servizi
Scopri
Chi Siamo
Back
Prodotti & Servizi
Back
Scopri
Ansys potenzia la nuova generazione di ingegneri
Gli studenti hanno accesso gratuito a software di simulazione di livello mondiale.
Back
Chi Siamo
Progetta il tuo futuro
Connettiti a Ansys per scoprire come la simulazione può potenziare la tua prossima innovazione.
Customer Center
Supporto
Partner Community
Contatta l'ufficio vendite
Per Stati Uniti e Canada
Accedi
Prove Gratuite

Ansys, part of Synopsys, has developed a model-based approach to establish a single design failure mode and effects analysis (DFMEA) solution inside Ansys medini analyze system-oriented safety analysis software that is particularly well suited to supporting the architecture and requirements of multiple programs across OEMs and tier suppliers. This solution has been developed with the infrequent user in mind, and is highly scalable to reach hundreds of design and quality engineers.
What is DFMEA?
Design failure mode and effects analysis is a well-established best practice within the automotive industry for systematically identifying and assessing risks associated with product design. The process enables engineering teams to anticipate what could go wrong, understand the underlying causes of potential failures, and evaluate the consequences of those failures at both system and vehicle levels.
Beyond risk identification, DFMEA provides a structured framework to assess how failures can be detected, how their effects may be mitigated, and most importantly, how design changes can be implemented to prevent failures that could impact reliability or safety before the product is released. By applying DFMEA early and iteratively throughout the development cycle, organizations can reduce technical risk, improve product robustness, and support compliance with functional safety and quality standards.
The cost of reliability-related issues can be significant, and these costs increase dramatically the later a problem is discovered in the development life cycle.
Key Challenges to Implementing DFMEA
A key challenge with DFMEA is to apply the process consistently across programs, regions, and engineering organizations. Traditional FMEA is typically spreadsheet-driven and document-centric, leading to differences in formats and interpretations across an organization. In addition, operating with a disconnected toolchain can make it difficult to maintain traceability, reuse knowledge, or ensure alignment as designs evolve. This fragmentation is exacerbated in global development programs, where time zone differences and regional engineering practices further complicate collaboration and governance. Such challenges can all contribute to causing variations in quality.
The Ansys Solution Established a Standard Quality Process
To apply a consistent DFMEA process across large, globally distributed teams, Ansys has developed an efficient and scalable approach inside Ansys medini analyze software using Systems Modeling Language (SysML)-based architecture models. The approach is able to harmonize multiple legacy worksheets, while aligning fully with the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) and Verband der Automobilindustrie (VDA) FMEA methodology.
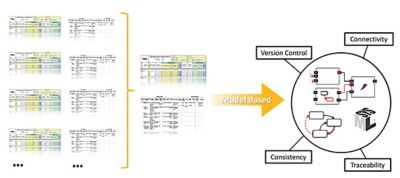
Consolidation and standardization of multiple DFMEA architectures and worksheets creating a model-based solution inside Ansys medini analyze software
Central to the Ansys solution is the use of system architecture and functional modeling as the foundation for DFMEA creation. Functional block diagrams defined at system, subsystem, and component levels are used to directly drive DFMEA worksheets, ensuring that failure analysis is rooted in design intent and remains consistent as architectures evolve. This model-based approach supports reuse, improves traceability, and reduces the risk of omissions that are common in document-centric DFMEA processes.
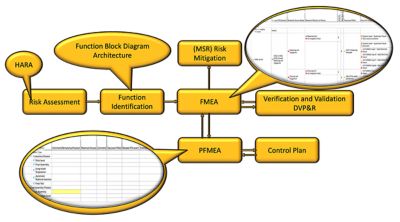
The DFMEA workflow process starts with a risk assessment to identify areas of focus. Beyond core DFMEA activities, the Ansys solution tightly integrates with a design verification plan and report (DVP&R).
The DFMEA implementation is built around a customized DFMEA template embedded within medini analyze software, replacing the multiple region-specific formats. Standardized libraries for failure modes, hazards, root causes, and prevention and detection controls are used to enforce consistency, while still allowing controlled extension where program-specific needs exist.
Prevention and detection controls, action priority evaluation, and risk mitigation actions are managed natively within the model, with automatic propagation of severities, occurrences, and design changes across hierarchy levels. Design validation plan and report (DVP&R) and functional characteristic artefacts are generated directly from DFMEA content and therefore automatically synchronized as designs and mitigation measures change. This linkage ensures strong alignment among identified risks, validation activities, and design controls throughout the development life cycle.
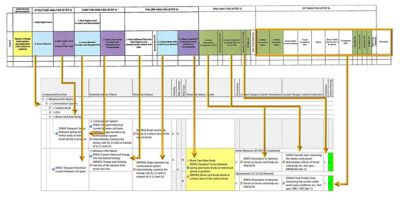
Top: AIAG-VDA Form Sheet; bottom: Ansys medini analyze software
The organization retains flexibility for legacy data and supplier collaboration through robust import and export capabilities, supported by scripted mappings for both harmonized and historical DFMEA formats. At the program level, medini analyze software provides aggregated KPIs and action tracking, enabling improved visibility of DFMEA maturity, open risks, and validation status across systems and vehicle programs.
This solution positions the medini analyze solution as more than a DFMEA authoring tool. It establishes DFMEA as a living, architecture-driven quality process, tightly integrated with validation planning and program governance, and scalable across regions, platforms, and product lines.
Collaborative DFMEA Improves Quality and Decreases Risk
A standardized, collaborative DFMEA tool is critical not only for engineering quality, but for managing downstream business risk. By providing a single, shared, and auditable view of design risks, failure chains, and mitigation decisions, organizations are far better equipped to demonstrate due diligence when responding to recall notices, regulatory scrutiny, or product liability claims. Consistent DFMEA data across programs and suppliers reduces ambiguity in root-cause analysis, accelerates containment decisions, and supports defensible warranty assessments.
At the same time, replacing fragmented, manual, spreadsheet-based FMEAs with a common, model-driven solution significantly reduces non-value-added engineering effort — eliminating rework, version conflicts, and repeated data entry. The result is not only fewer late-stage quality issues, but measurable gains in engineering efficiency, enabling teams to focus on design improvement rather than document maintenance.
The Advantage Blog
The Ansys Advantage blog, featuring contributions from Ansys and other technology experts, keeps you updated on how Ansys simulation is powering innovation that drives human advancement.