-
-
Accédez au logiciel étudiant gratuit
Ansys donne les moyens à la prochaine génération d'ingénieurs
Les étudiants ont accès gratuitement à un logiciel de simulation de classe mondiale.
-
Connectez-vous avec Ansys maintenant !
Concevez votre avenir
Connectez-vous à Ansys pour découvrir comment la simulation peut alimenter votre prochaine percée.
Pays et régions
Espace client
Support
Communautés partenaires
Contacter le service commercial
Pour les États-Unis et le Canada
S'inscrire
Essais gratuits
Produits & Services
Apprendre
À propos d'Ansys
Back
Produits & Services
Back
Apprendre
Ansys donne les moyens à la prochaine génération d'ingénieurs
Les étudiants ont accès gratuitement à un logiciel de simulation de classe mondiale.
Back
À propos d'Ansys
Concevez votre avenir
Connectez-vous à Ansys pour découvrir comment la simulation peut alimenter votre prochaine percée.
Espace client
Support
Communautés partenaires
Contacter le service commercial
Pour les États-Unis et le Canada
S'inscrire
Essais gratuits
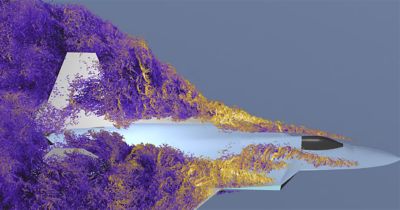
In aerospace and defense (A&D), computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is central to solving multidisciplinary design challenges ranging from aeroacoustic noise reduction to high-fidelity thermal modeling. As simulation fidelity increases, so do computational demands, and traditional CFD workflows are no longer sufficient. To address these challenges, recent advancements in solver architecture, meshing automation, and artificial intelligence (AI) integrations are fundamentally reshaping aerospace simulation.
The shift from CPU- to GPU-based solvers is resulting in massive simulation solve time improvements. In the above case, a 600-million-cell model was solved in just 14 hours on 20 NVIDIA L40 GPU cards.
From CPU- to GPU-Based CFD Solvers
Historically, solver speed and memory efficiency have been bottlenecks in large-scale CFD, especially for unsteady, scale-resolving simulations like large eddy simulation (LES) and discrete-event simulation (DES). CPU-based simulations for these types of problems can last weeks and sometimes months, forcing CFD engineers to weigh the trade-offs of a more accurate, high-fidelity simulation versus a less accurate, lower-fidelity simulation. As computational architectures shift from CPU-centric to GPU-accelerated hardware, engineers no longer have to make these kinds of trade-offs.
Recent developments in native GPU-based CFD solvers written specifically to utilize GPU parallelism, including the Ansys Fluent native GPU solver, shortens simulation runtimes exponentially from weeks or months to hours or days while enabling larger-scale models at higher levels of fidelity.
Read the Fluent GPU solver FAQ article to learn more.
Benchmark data for aerospace CFD simulations run on GPU hardware show significant acceleration:
- LES simulations that took over two days to run on 1,000 CPUs can now be completed in under two hours using 32 GPUs.
- Wall-modeled LES for full-aircraft aerodynamics — including pitch, drag, and lift fidelity — has been demonstrated at industrial scale within practical runtimes.
This enables transient, high-resolution CFD studies that were previously computationally prohibitive. Simulations that used to be “hero” calculations — simulations that would take months to solve or converge — are now being completed in a few working days.
Meshing at Speed and Scale: Octree-Based Automation
Mesh generation has traditionally been a labor-intensive task, particularly for complex aerospace geometries with sharp leading edges, fine boundary layers, and multicomponent assemblies. Recent developments in rapid octree-based meshing algorithms offer a more automated alternative.
The rapid octree mesh approach uses a Cartesian-based cell structure with local refinement based on geometric curvature and flow features. Benefits include:
- Fully parallelized mesh generation on CPU clusters
- Robust handling of dirty or complex computer-aided design (CAD) geometry
- Prism layer extrusion for turbulence modeling (e.g., Reynolds-averaged Navier-Stokes, LES)
This means that not only are meshing times much faster, but you can also mesh previously prohibitively large models quickly. For example, a full-scale aircraft geometry with tens of millions of cells, typically requiring hours to mesh, can be meshed in under an hour using 500-plus cores. This is particularly useful for scale-resolving simulations in which larger meshes are required.
Access the rapid octree meshing help documentation to learn more.
A New Era in CFD: Mesh in Minutes, Solve in Hours
Combining rapid octree meshing automation with the Fluent native GPU solver results in some impressive meshing and simulation speeds:
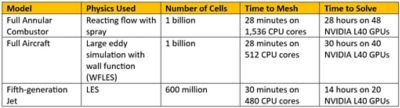
What used to take weeks or months to solve can now be completed in one to two working days. This is fundamentally changing the CFD landscape and the industries that use CFD to design and optimize their products.
Imagine a future in which aerospace applications, such as full-aircraft LES simulations like those in the table above, are commonplace. With the adoption of appropriate hardware and technology, engineers and manufacturers will be able to experience much faster design cycles through faster virtual prototyping. This will result in more time spent on optimization and analysis and new, more sustainable innovations before a physical product is built.
Read the blog “A New Era of Ansys Fluent Computations” to learn more.
AI-Augmented Workflows: Accelerating Design Insights
Ansys is actively integrating AI and machine learning (ML) techniques to enhance CFD workflows. These capabilities accelerate and optimize key steps in simulation setup, execution, and analysis.
- CFD AI+: equips users to apply ML-based tuning coefficients for turbulence modeling. Improves solution accuracy and fidelity while maintaining the computational cost of lower fidelity (often steady-state methods). In other words, results approach LES accuracy at a RANS computational cost.
- Ansys SimAI cloud-enabled AI platform: provides data-driven insights based on your legacy simulation data. Upload data, select relevant design outputs, and generate your AI model. Explore performance for new geometries and flow conditions in minutes without simulation expertise required.
Adopting these technologies will result in faster and more accurate simulations on top of the already-massive time savings enabled by rapid octree meshing and GPU-accelerated solvers.
Dedicated Aerospace and Defense GUIs
Fluent software is particularly dedicated to A&D engineers. Within the Fluent launcher are two dedicated workspaces for A&D engineers: the Fluent Aero workspace and the Fluent Icing workspace.
The is a specialized environment within Fluent software tailored to A&D external aerodynamic simulations. It integrates preconfigured workflows, mesh adaptation strategies, solver settings, and automated post-processing tools to efficiently set up and execute complex CFD studies. Its capabilities include:
- Automated solver setup: the latest density-based solver and convergence enhancements tuned for external aerodynamics
- Flight conditions: parametric support for Mach sweep, pitch and yaw angle variation, and altitude with built-in atmospheric properties
- Post-processing: automated drag, lift, and pitching moment calculations with plots and contours; body-fixed or wind-fixed aero coefficients
- Advanced workflows: constant lift flight condition, automated mesh adaption, propeller and rotor blade aerodynamic extraction, and data export to the Ansys Systems Tool Kit (STK) Aviator tool and Ansys HFSS high-frequency electromagnetic simulation software
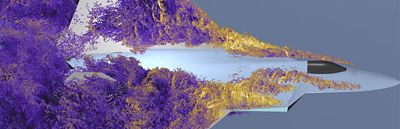
Results of a mesh adaption study in the Fluent Aero workspace using six combined Hessian indicator adaption cycles that show successive mesh refinement improvements to capture the wake
Using the Fluent Aero workspace, engineers can run a full-aircraft flight envelope with turbulent transition and shock-boundary layer interactions and get post-processed lift and drag data within a workflow purpose-built for flight certification support.
The Fluent Icing workspace offers a focused environment for modeling in-flight icing phenomena, which is critical for aircraft certification and safety assessments. It is based on the physics of supercooled droplet impingement, phase change, and surface roughness and ice accretion dynamics. Fluent Icing incorporates the state-of-the-art icing models of Ansys FENSAP-ICE in-flight aircraft icing simulation software.
- Droplet impingement models: Eulerian (DROP3D) and Lagrangian (DPM) particle tracking, including particle thermal energy and water vapor transport for ice crystal melting, droplet evaporation and freeze-out
- Supercooled large droplet (SLD) and ice crystals: SLD modeling with droplet breakup, surface splashing and bouncing, ice crystal sticking efficiency based on melt fraction, splashed particle reinjection and re-impingement, and ice crystal shattering
- Icing cloud concentration factor analysis, shadow, and enrichment zones
- Ice growth models: Eulerian PDE-based runback water film including rotational and gravitational forces; unified thermodynamic model for rime, glaze, and mixed ice shapes; mesh morphing or remeshing for two-way coupling of ice growth with air and droplet flows
- 3D ice shape capabilities: high-fidelity scallop ice shapes on swept wings using the multishot with remeshing workflow
- Ice shedding: natural ice shedding with rotational forces on rotating components like propellers, wind turbines, engine fans, etc.
- Thermal ice protection system analysis: hot-air anti-icing with runback ice prediction, electro-thermal de-icing with melt or shed models
- Engine icing: Ansys CFX CFD software multi-row grid and solution import into Fluent Icing, Lagrangian tracking for droplet and ice crystal ingestion, particle size distribution evolution through engine rows, three-layer ice crystal icing model to predict build-and-shed or constant accretion behavior of ice crystals in warm engine components
- Certification alignment: workflow support for Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) icing envelope testing, an aid-to-certification tool to shift design space exploration from wind tunnel to software that helps engineers optimize the time spent in wind tunnels and conducting actual flight tests
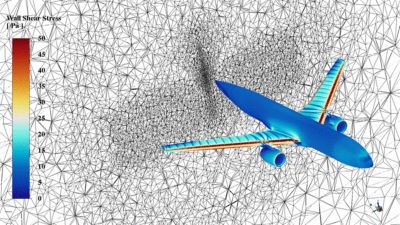
Ice accretion simulation on a swept aircraft wing using the Ansys Fluent Icing workspace
The Future of A&D and GPU-Powered Simulation
The accelerating pace of innovation in aerospace demands tools that empower engineers to move faster without sacrificing accuracy. Fluent software — through native GPU solvers, automated meshing, AI-augmented workflows, and dedicated A&D GUIs — is transforming how we approach high-fidelity CFD.
What once required weeks of manual effort and compute time can now be achieved in hours or days, which lets engineers focus more on iteration, optimization, and achieving certifiable results. As simulation becomes faster, smarter, and more scalable, the path from concept to flight is becoming not just shorter, but smarter. The future of aerospace CFD isn’t just approaching — it’s already here.
The Advantage Blog
The Ansys Advantage blog, featuring contributions from Ansys and other technology experts, keeps you updated on how Ansys simulation is powering innovation that drives human advancement.